Corticospinal pathways > Pyramidal decussation in medulla
Corticospinal pathways > Pyramidal decussation in medulla
Corticospinal pathways > Pyramidal decussation in medulla > animation
Click/tap on the picture 20 times to advance the animation. Wait for each action potential to reach it's destination before clicking/tapping again. Click/tap once more to re-start the animation.
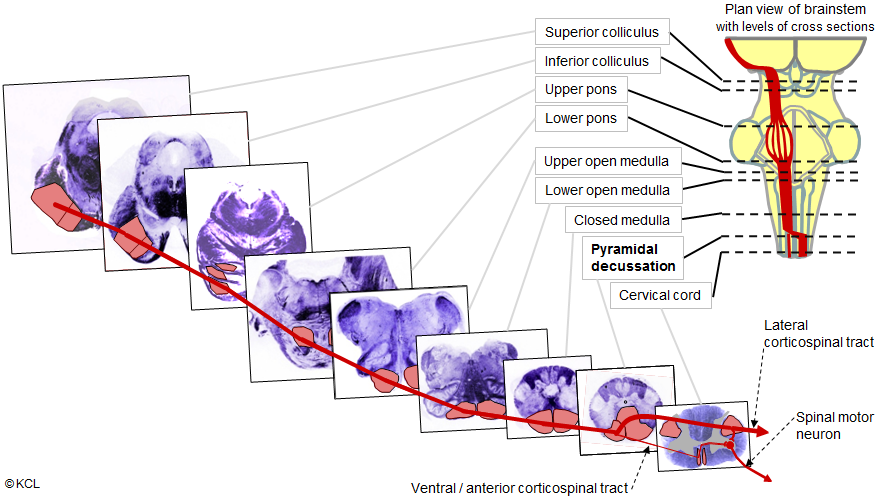
This image is of the corticospinal pathway through the brainstem, shown in a series of transverse cross sections - note the position of the pyramidal decussation in the medulla.
Pyramidal decussation of the lateral corticospinal tract:
- The lateral corticospinal tract is the major pathway for voluntary movement, with axons originating from motor centres of the cerebral hemispheres and terminating directly or indirectly on spinal motor neurons supplying the body's muscles. Any injuries which affect its functioning result in paralysis.
- This pathway descends through the brainstem then the axons of the tract cross sides in the ventral part of the medulla and enter the lateral column of the spinal cord. The crossing is termed the pyramidal decussation (because it is formed between the two longitudinal ridges (called pyramids) on the ventral surface of the medulla.
- Lesions of the tract above the decussation cause paralysis on the side opposite to the lesion, lesions of the spinal cord, below the decussation, cause paralysis on the same side as the lesion (see 1.4).
