Functional Aspects of Muscle Spindles: Effect of Stretch on spindle sensory discharges
As you will realise if you look at the results summarised in the sections describing responses obtained from terminals located on the different intrafusal fibre types, these responses are very different, and the changes elicited by fusimotor supply also vary. What ‘take home’ points can be extracted from them?
1. Primary endings give uniquely non-linear responses, and may be 100x more sensitive to small stretches than large ones.
2. When a Db1 fibre is activated by a dynamic gamma axon there is little extension of primary ending but the stiffness of the contracting capsular sleeve and extracapsular regions is enhanced so that more applied stretch reaches spiral .. i.e. Ia discharge is increased. Fusimotor activity in the Db1 fibre greatly increases the sensitivity of the primary ending to length changes during movement. Secondaries if present will experience a similar effect but to a lesser extent.
3. Stretch of active Sb2 fibres has a negligible effect on primary spiral, which is already greatly extended by the static fusimotor activity alone. and as a result although discharge rates increase due to the fusimotor drive, the sensitivity to length changes is reduced. Similar but smaller effects on secondaries which are appreciable in number.
4. Fusimotor stimulation of chain fibres applies a large positive bias to the discharge of both primary and secondary endings. Static and dynamic length sensitivity of primaries is disrupted, that of secondaries is enhanced.
To simplify first consider all intrafusal fibres inactive, i.e. no fusimotor input (passive spindle). Consider ramp stretch, hold, ramp unstretch.
Primary endings discharge at high frequency during stretch and fall silent during release, secondary endings have less marked increase in discharge during stretch and continue to fire during release. Both show a linear rise in discharge frequency during the stretch, represented by an offset straight line. Offset and slope depend on velocity of stretch. Response is proportional to product of a length term and velocity term ( l × v ·³ ). Slope of response during stretch gives measure of length sensitivity under dynamic conditions. Difference between initial and final adapted frequencies indicates length sensitivity under static conditions. Fusimotor activity modifies dynamic and static length sensitivities, not velocity sensitivity.
Right at the start of a stretch there is a brief rapid discharge (a similar rapid fall at end of stretch). This effect is more noticeable in primaries. Usually attributed to stiction.
During the plateau of applied stretch there is adaptation lasting several seconds. The discharge falls with maintained stretch. This effect is very small in most primaries, and is due to mechanical creep in Db1 fibre. The more pronounces slow adaptation in secondaries is probably ionic in origin.
Primaries are uniquely non-linear, may be 100x more sensitive to small stretches than large ones.
Afferent responses to stretch during fusimotor activity
Large ramp on Primary and Secondary endings during max activation of Db1 and Sb2 and chain fibres compared.
When a Db1 fibre is activated by a dynamic gamma axon there is little extension of primary ending but the stiffness of the contracting capsular sleeve and extracapsular regions is enhanced so that more applied stretch reaches spiral .. i.e. Ia discharge is increased. When held at a new length there is creep which is the basis of the considerable mechanical adaptation resulting in an adapted discharge that is not greatly different to the situation of no fusimotor input. Fusimotor activity in the Db1 fibre greatly increases the sensitivity of the primary ending to length changes during movement. Secondaries if present will experience a similar effect but to a lesser extent.
Stretch of active Sb2 fibres has a negligible effect on primary spiral, which is already greatly extended by the static fusimotor activity alone. Much of the stretch seems to be accommodated by the extracapsular region. Fusimotor activity in the Sb2 fibre greatly increases the discharge of the primary ending whilst reducing its sensitivity to static and dynamic length changes. (to put it another way, big DC offset but reduced gain). Similar but smaller effects on secondaries which are appreciable in number.
Fusimotor activity in chain fibres applies a large positive bias to the discharge of both primary and secondary endings. Static and dynamic length sensitivity of primaries is disrupted, that of secondaries is enhanced.
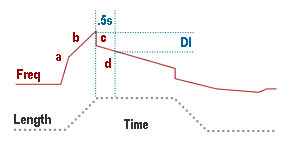
Dynamic index
The fall in discharge frequency in the first 0.5 sec following the completion of a ramp stretch. Several factors contribute:
- Peak discharge freq. depends on amplitude of initial fast rise phase
- and the slope of the response during stretch ,
- the amplitude of the fast fall phase
- and the slow adaptation of whatever origin .
a. and c. may have an ionic basis. b is explained mechanically.
Select another item from the menu on left to continue.