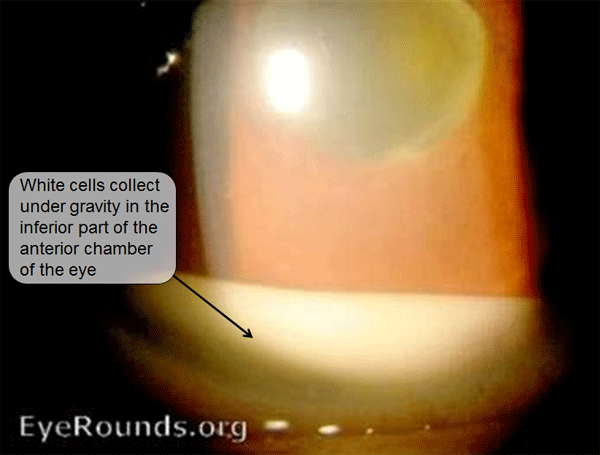
Anterior Uveitis
Multiple causes and associations:
- Idiopathic Most common (no associated systemic disease)
- Autoimmune HLA B27 Ankylosing spondylitis, Reiter syndrome, psoriatic arthritis
- Juvenile chronic arthritis
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Non infectious systemic disease Sarcoidosis, Behcets, MS
- Infections Syphilis,TB, herpes zoster and herpes simplex,
- Traumatic
- Post operative
Symptoms
- Unilateral or bilateral
- Red eye
- Pain
- Photophobia
- Tearing
- Normal to mildly decreased vision
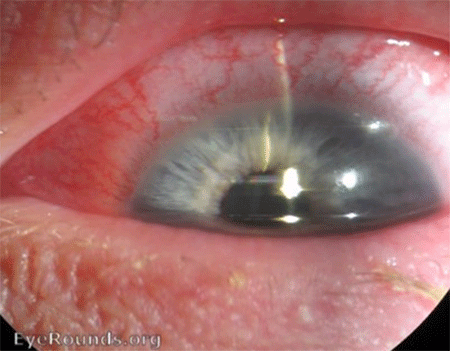
Signs
- Circum-corneal injection
- Keratic precipitates
- Watery discharge
- Possible constricted or distorted pupil
- Hypopyon
Complications
- Posterior synechiae
- Secondary glaucoma
- Secondary cataract
Workup
- Complete ocular history and exam
- Systemic history and exam for various associated conditions
Treatment
Attacks usually last from several days to 6 weeks. The majority of patients are managed with topical steroids and cycloplegia