- Key Concepts
- Animation
Corticospinal pathways > projected onto brain
KEY CONCEPTS
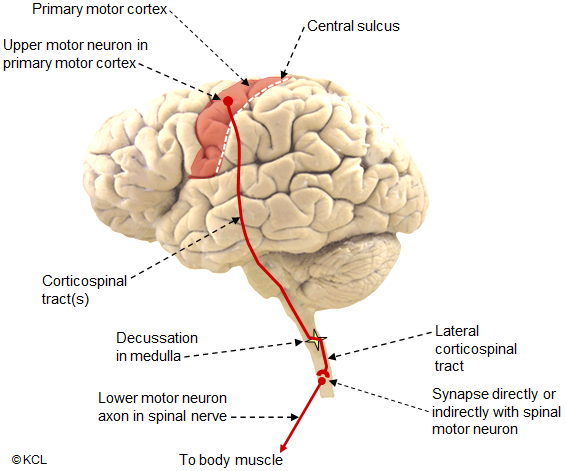
This is a lateral view of the brain and upper spinal cord, indicating the pathway of the corticospinal tract from the primary motor cortex via the spinal cord to the periphery. Note: the tracts are deep within the brain, not on the surface as shown here.
The corticospinal pathway:
- Carries voluntary motor commands.
- Controls spinal reflexes.
- Has each axon begining in the motor cortex and terminating in the spinal cord at or near its target lower motor neuron.
- Has most (~85%) of its axons crossing sides in the ventral medulla (decussation of the pyramids) to create the lateral cortico-spinal tract.
- Has a few (~15%) of its cortico-spinal axons (forming the anterior/ventral cortico-spinal tract) that stay on the same side but eventually cross in the spinal cord near their termination (not shown in this picture).
Corticospinal pathways > projected onto brain
Click/tap on the image 4 times to advance the animation. Wait for each action potential to reach its destination at the end of the neuron before clicking/tapping again. Click/tap once more to re-start the animation.
Select one of the tabs above, or choose a menu item to the left, to continue