|
|
|
 |
|
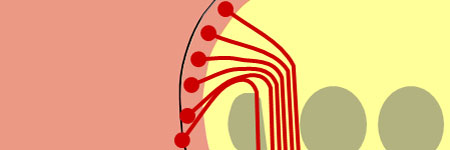 |
- The motor systems of the brain and spinal cord are either voluntary or involuntary.
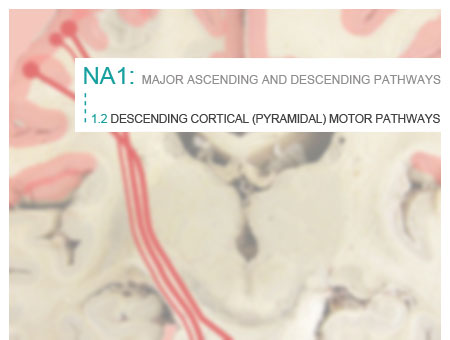
- Voluntary muscle contraction results from commands initiated in the cerebral cortex and carried by the cortico-spinal pathway (for the body), and cortico-bulbar pathway (for most head muscles). These are are called the pyramidal pathways since all the cortico-spinal axons and some cortico-bulbar axons pass through the pyramids in the medulla.
- Pyramidal axons typically decussate at some point along their pathway, most of the cortico-spinal axons in the ventral medulla, and cortico-bulbar axons at various levels of the brainstem near their terminations. Some cranial nerve motor nuclei receive cortico-bulbar axons from both motor cortices.
- NB: Involuntary motor systems include reflex pathways of the spinal cord and brain, some local (e.g. Spinal reflexes) and some descending from the brainstem, [see 1.3] or are concerned with homeostasis, such as the control of respiratory movements, autonomic control of smooth muscle, etc.
|
|
|
 |
|
|
© King's College London 2011 | Content & original graphics by Professor Lawrence Bannister | Interface design & development by EHM, CTEL | Content development by Julia Warner, VC TEL |