- Key concepts
- Animation
Lesions to lateral corticospinal tract: below pyramidal decussation
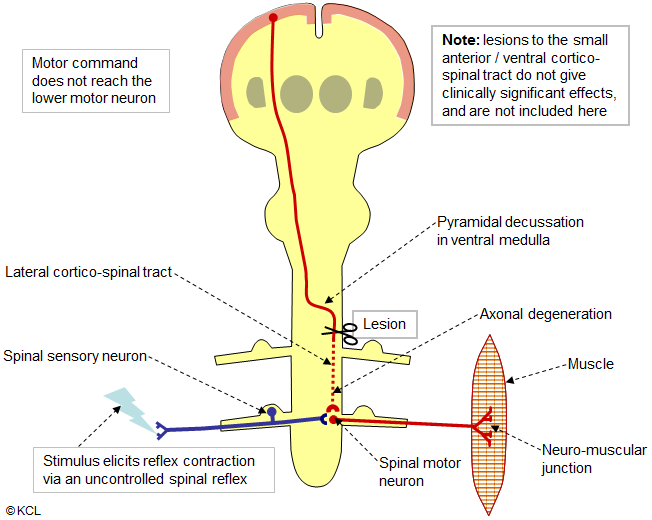
RESULT: Ipsilateral spastic paralysis
- Muscle tone increases.
- Reflexes are still intact, but now, lacking descending control, they are exaggerated.
- Muscle fibres do not fasciculate or waste away.
- Paralysis of muscles occurs on the side contralateral to the lesion, below the lesion, as axons have already crossed over.
Select one of the tabs above, or choose a menu item to the left, to continue
Lesions to lateral corticospinal tract: below pyramidal decussation
Click/tap on the image 5 times to advance the animation. Wait for each action potential to reach its destination at the end of the neuron before clicking/tapping again.
RESULT: Ipsilateral spastic paralysis
- Muscle tone increases.
- Reflexes are still intact, but now, lacking descending control, they are exaggerated.
- Muscle fibres do not fasciculate or waste away.
- Paralysis of muscles occurs on the side contralateral to the lesion, below the lesion, as axons have already crossed over.
Select one of the tabs above, or choose a menu item to the left, to continue