- Key Concepts
- Animation
Lesion to a spinal motor neuron
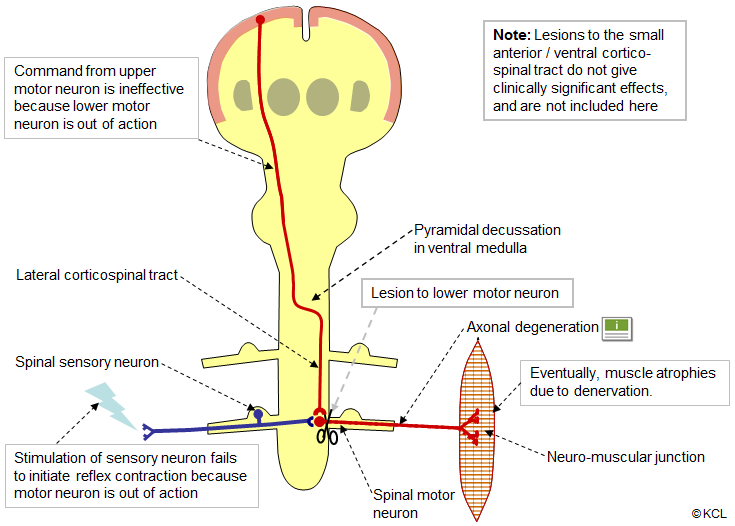
RESULT: Ipsilateral flaccid paralysis
- Affected muscles lose tone (i.e. are flacid) and reflexes are reduced or lost (spinal or brainstem reflex pathway is interrupted, so reflex cannot be elicited).
- Muscle fibres fasciculate (twitch spontaneously) and later atrophy.
- Flaccid paralysis of muscles occurs on the same side as the lesion, at the level of the lesion.
Lesion to a spinal motor neuron
Click/tap on the image 5 times to advance the animation. Wait for each action potential to reach its destination at the end of the neuron before clicking/tapping again.
RESULT: Ipsilateral flaccid paralysis
- Affected muscles lose tone (i.e. are flacid) and reflexes are reduced or lost (spinal or brainstem reflex pathway is interrupted, so reflex cannot be elicited).
- Muscle fibres fasciculate (twitch spontaneously) and later atrophy.
- Flaccid paralysis of muscles occurs on the same side as the lesion, at the level of the lesion.
Select one of the tabs above, or choose a menu item to the left, to continue