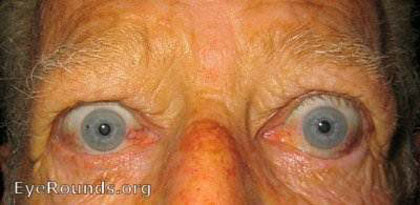
5: Ptosis
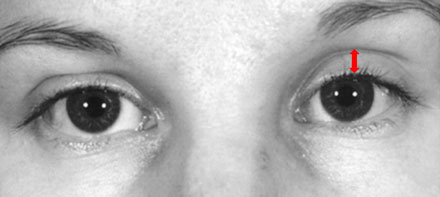
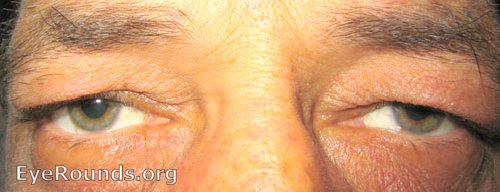
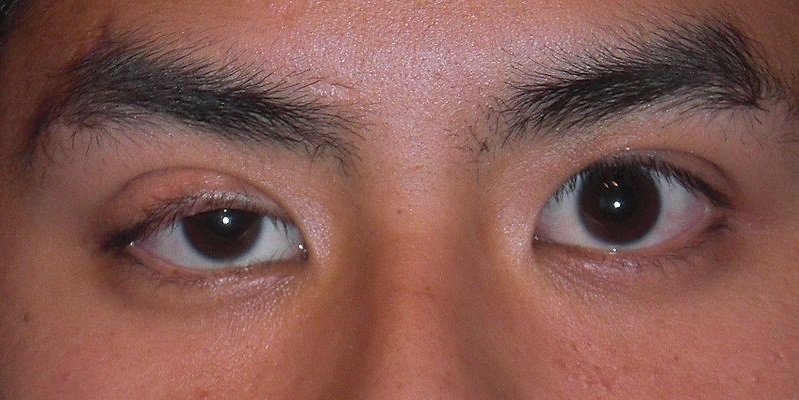
Ptosis means drooping of the upper eyelid. It may be unilateral, bilateral or asymmetric.
Source: Andrewya, Wikimedia. CC Public Domain.
The eyelid is elevated by the levator muscle, which is innervated by the 3rd cranial nerve. Normally the upper eyelid covers the top 1-2mm of the cornea. Children who have a ptosis are at risk of amblyopia if the eyelid obscures the pupil.
Symptoms
- Heavy eyelid
- Visual field reduced if obscures pupils
Patient Assessment
- Confirm that it is a true ptosis
- Establish if congenital or aquired
Differential Diagnosis
The following can create the false impression of ptosis:
- Enophthalmos
- Dermatochalasis
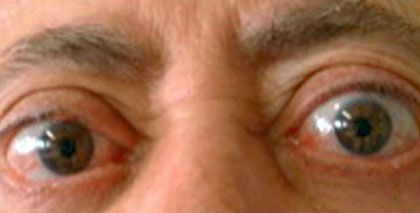
- Contralateral eyelid retraction
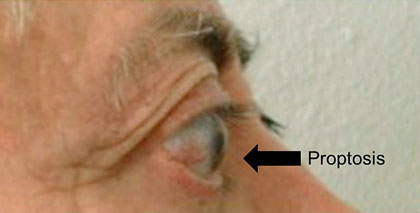
- Contralateral proptosis