5: Ptosis
Presentations
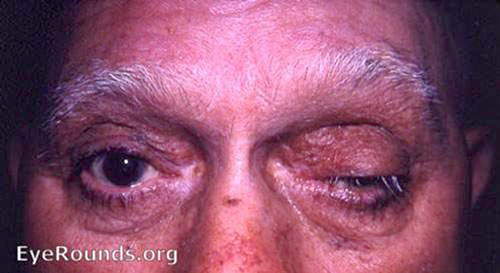
a) Left Partial ptosis

Reproduced from Cluster headache, Alexander D Nesbitt, Peter J Goadsby 2012;344:e2407. BMJ Publishing Group Ltd
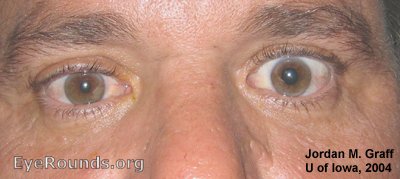
b) Bilateral partial ptosis

Reproduced from Botulism: a rare complication of injecting drug use, TN Wenham, Emerg Med J 2008;25:55-56. BMJ Publishing Group Ltd
c) Total left ptosis
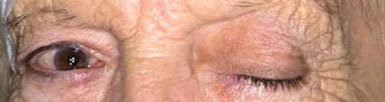
Reproduced from An unusual cause of bilateral ophthalmoplegia, Katherine L Warburton, Elizabeth Austen, Andrew Gough, Gunther E Wihl BMJ Case Reports 2010. BMJ Publishing Group Ltd
Causes
- Congenital
- Levator dystrophy
- Horner's syndrome
- Levator disinsertion (aponeurotic ptosis)
- Age (involutional)
- Trauma
- Mechanical due to an eyelid tumour
- 3rd nerve palsy
Usually also a divergent squint and the pupil may be dilated and unreactive
- Myasthenia gravis
Variable ptosis, becoming worse with effort and especially at the end of the day.
- Horner's syndrome
Accompanied by a small pupil and possibly loss of sweating on the affected side of face
- Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia (CPEO) (mitochondrial myopathy)