Can X-rays cause harm?
- Xrays absorbed by the body release energy and cause ionisation
- Ionisation is the release of electrons from atoms leading to chemical and/or biological change

Effects of X-rays passing through cells
X-rays passing through the cell
There are three possible effects when X-rays pass through a cell:
- No effect
- The cell dies
- DNA damage is caused (which can result in genetic mutation and a risk of cancer)
The risk of DNA damage is greatest in rapidly dividing cells e.g. Testes, ovaries and developing embryos
Radiation Doses
Radiation is actually all around us and the highest dose of radiation received by people is from natural background radiation.
- Radon gas in atmosphere (58%)
- Cosmic rays from space (14%)
- Ground rocks (16%)
- Food (12%)
Medical X-rays/ nuclear medicine studies give an additional small dose, which means there is only a small additional risk of cancer in future!

A 4 hour flight has the same radiation as a chest X-ray!
Click on an individual tab to see the risk of radiation which each type of X-ray:
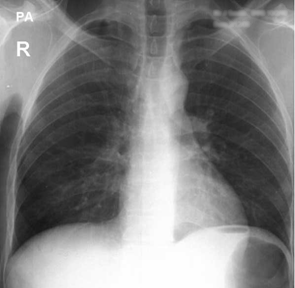
| Dose | Background radiation (equal to) | Risk of cancer |
|---|---|---|
| 0.03mSv | 3 days | < 1 in 1,000,000 |
The dose of a chest x-ray is the equivalent dose of 3 days background radiation.
The risk of developing cancer from having a chest x-ray is fairly low at less than one in a million.
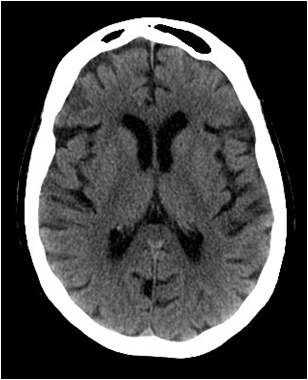
| Dose | Background radiation (equal to) | Equivalent X-rays | Risk of cancer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2mSv | 6 months | 60 CXR | 1 in 10,000 to 1 in 100,000 |
The dose from CT is higher than from plain x-rays. The dose of a CT is equivalent in dose to 60 chest x-rays and 6 months background radiation.
Because of this increase in radiation dose, the risk of developing a potential cancer is slightly increased.
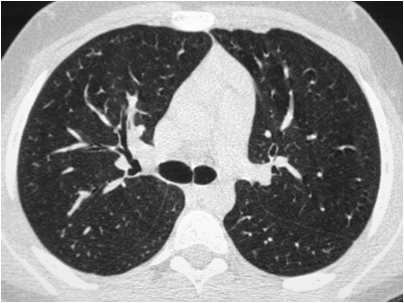
| Dose | Background radiation (equal to) | Equivalent X-rays | Risk of cancer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7mSv | 2 years | 250 CXR | 1 in 1,000 to 1 in 10,000 |
Radiation dose is again increased with CT to the torso.
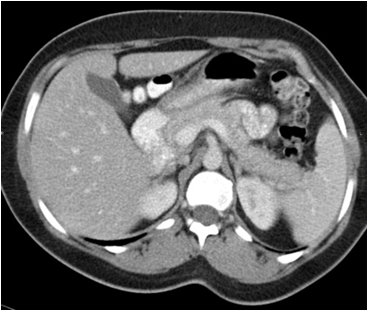
| Dose | Background radiation (equal to) | Equivalent X-rays | Risk of cancer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mSv | 3 years | 300 CXR | 1 in 1,000 to 1 in 10,000 |
Radiation dose is again increased with CT to the torso. With scans that involve the pelvis there is additional risk of radiation exposure to reproductive organs.
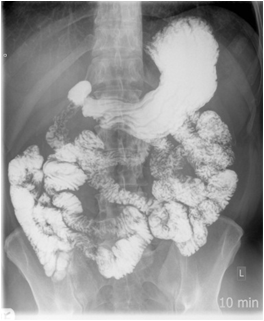
| Dose | Background radiation (equal to) | Equivalent X-rays | Risk of cancer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mSv | 3 months | 30 CXR | 1 in 10,000 to 1 in 100,000 |
Barium screening studies which are dynamic x-ray investigations, again carry a significant associated radiation dose.
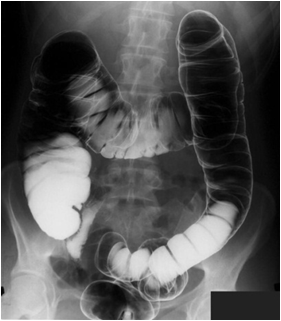
| Dose | Background radiation (equal to) | Equivalent X-rays | Risk of cancer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mSv | 3 years | 300 CXR | 1 in 1,000 to 1 in 10,000 |
Barium screening studies which are dynamic x-ray investigations, again carry a significant associated radiation dose.
