Myocardial Ischemia Versus Myocardial Infarction
- Myocardial Ischemia / Myocardial Infarction
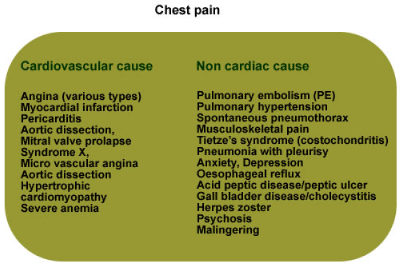
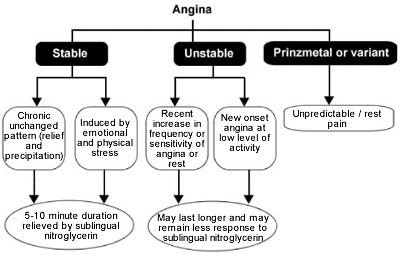
- Angina pectoris
Gross/macroscopic characteristics of myocardial infarction:
- Is not identifiable within the first 12-18 hours
- Shows pallor in about 24 hours post infarction (gradually acquires a mottled appearance)
- Is sharply defined outline with a hyperemic border (highly vascularised granulation tissue) in 3-7 days post infarction
- Is depressed and soft in 2-3 weeks and fibrous scar develops in a few weeks
The difference between myocardial ischemia and myocardial infarction is that in the case of myocardial ischemia, the amount of oxygen supplied to the tissue is inadequate and in general, if the blood flow to the tissue is improved, myocardial ischemia is reversible.
Myocardial infarction on the other hand, is where the tissue has undergone irreversible death due to lack of oxygen-rich blood.
Complications of myocardial infarction:
- Myocardial rupture
- Right ventricular infarction
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
- Ventricular aneurysm
- Pseudoaneurysm
- Dressler's syndrome (Post-MI syndrome)
- Arrhythmias
- Heart failure or frank cardiogenic shock
- Papillary muscle rupture leading to valvular incompetence