Test Your Numeracy ...
 Virtual Campus
Virtual Campus  Print
Print Calculator
Calculator 
- HOME
- Units, symbols and indice
- Concentration Ratios
- Percentage w/v and Content example
- Vitamin pill dosage
- Percentage concentration & Molarity examples
- Lethal Volume
- Morphine Injection
- Parts per million and molarity
- Making up saline solutions
- Making up various solutions
- Body Mass Index
- Dye dilution (to measure body fluid spaces)
- Nerve Conduction Velocity (time, distance and speed)
- Nernst Equation(log friendly)
Nerve Conduction Velocity
 This shows part of an MSK examination
question for Medicine Year 1. A substantial number of students failed to get
the calculation right, either because of arithmetical errors, or because of
a confusion about units (milliseconds vs seconds, etc)
This shows part of an MSK examination
question for Medicine Year 1. A substantial number of students failed to get
the calculation right, either because of arithmetical errors, or because of
a confusion about units (milliseconds vs seconds, etc)
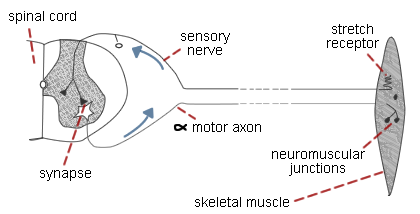
The diagram to the right illustrates a simple reflex loop involved in controlling the length of a skeletal muscle. Stretch of the muscle is detected by stretch receptors embedded in the muscle and this triggers an action potential in the sensory nerve. This nerve enters the spinal cord via the posterior (dorsal) root and synapses with an alpha motor neuron. Release of the neurotransmitter from the sensory neuron terminals triggers an action potential in the motor neuron, leading to contraction and thus shortening of the muscle.
The approximate length of the nerves is 500 mm each. Assuming that:
- a) conduction velocity in the sensory nerve axons is 100 m.sec-1
- b) conduction velocity in the motor axons is 70 m.sec-1,
- c) each synapse introduces a delay of 1 msec