Test Your Numeracy ...
 Virtual Campus
Virtual Campus  Print
Print Calculator
Calculator 
- HOME
- Units, symbols and indice
- Concentration Ratios
- Percentage w/v and Content example
- Vitamin pill dosage
- Percentage concentration & Molarity examples
- Lethal Volume
- Morphine Injection
- Parts per million and molarity
- Making up saline solutions
- Making up various solutions
- Body Mass Index
- Dye dilution (to measure body fluid spaces)
- Nerve Conduction Velocity (time, distance and speed)
- Nernst Equation(log friendly)
Nernst Equation
 The
Nerst Equation is unpopular with students for 2 reasons
The
Nerst Equation is unpopular with students for 2 reasons
- a)
It is an equation. Students don't like these
- b) It has logs in it (also why pH is unpopular)
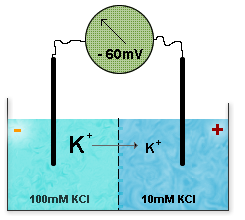
Which is a pity, because playing with it helps consolidate the basic ideas about what is going on in a cell at rest and when it starts to let various ions in (or out).
In its Physiology Friendly approximation it is very easy to use.
![Vm = 60 log [X+]o over [X+] i mV](images/Nernst-equation.png)
Which says that if a membrane is selectively permeable to an ion X, which is at a different concentration (square brackets) outside and inside(o and i), then at equilibrium when the tendency to equalise concentrations is balanced by the electrical consequences) a voltage will appear across the membrane (Vm, in millivolts).