Introduction to Gating
- Gating
- Image acquisition
Some facts about gating:
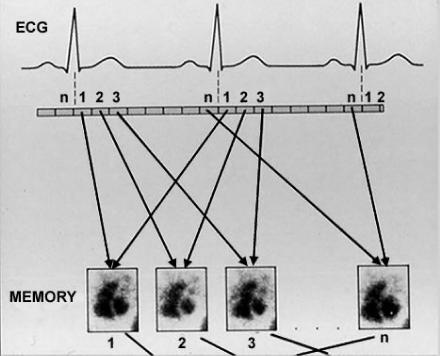
- Gating involves the acquisition of images in conjunction with ECG
- Images are synchronised using ECG–R wave as a reference point
- Each cardiac cycle (R-R int) is divided into 16-64 frames (gen-18)
- Each frame is sorted according to the the position in the cardiac cycle
Different gating techniques:
- Frame mode: This is where each frame is directly stored in a temporary memory buffer during acquisition. This is averaged over 300-600 cardiac cycles to produce a single cardiac cycle
- List mode: This is where each scintillation event is stored along with x and y co-ordinates, the timing marker in the R-R interval. Sorting is done retrospectively
- Fixed beats: 300-800 beats. The heart rate is initially sampled for 10-20 seconds and mean R-R interval is determined. Any beat which is 10% longer or shorter than the mean is rejected. The window should not exceed 30% if meaningful data is to be acquired
- Fixed counts: Study is acquired for about 4-6 million counts