Unit 1: Sudden Loss of Vision
2: Giant cell arteritis
Introduction
Giant cell arteritis is a rare but important disease, also called temporal arteritis. It presents with sudden painful loss of vision. Giant cell arteritis is an emergency as the other eye can develop loss of vision within hours. It usually effects patients 50 years and older and has a female preponderance. It is associated with polymyalgia rheumatica.
Giant cell arteritis is a vasculitis of the medium and large arteries. It often affects arteries around the temple, scalp, head and neck. The optic nerve head blood supply is compromised, producing anterior ischaemia optic neuropathy. Therefore it has a similar presentation to non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, but is more likely to have pain and raised ESR/CRP.
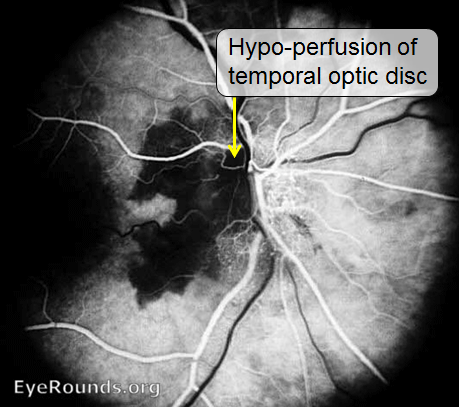
Fluorescein angiogram shows ischaemia of the optic disc and surrounding choroid