Unit 1: Sudden Loss of Vision
1: Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy
Management
- Refer to Ophthalmology urgently, to exclude giant cell arteritis (link opens in a new Window/tab) with examination /ESR/CRP
- Review and treat all cardiovascular risk factors
- Consider aspirin
Prognosis
- 30% make substantial improvement (gain of 3 lines on a Snellen vision chart)
- 15-50% risk to fellow eye
- The optic disc swelling gradually resolves, leaving optic disc pallor (due to loss of neural tissue)
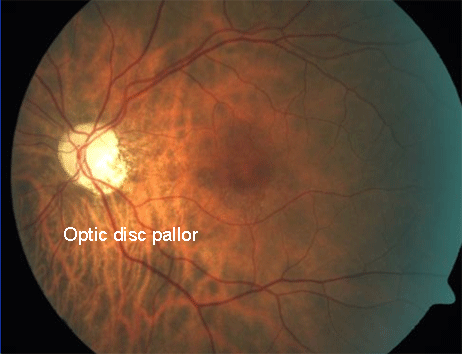
Optic disc pallor
Source: www.retinagallery.com