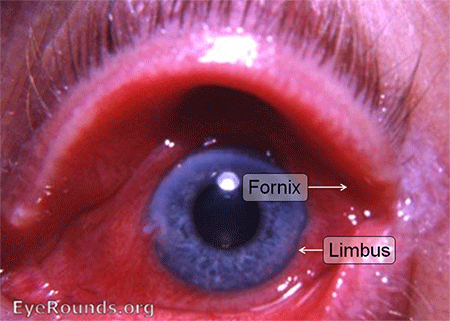
7: Herpes Zoster
Aetiology
- Herpes Zoster (Shingles) is a common unilateral infection caused by the zoster-varicella virus, it typically affects the elderly.
- 15% affect the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve (herpes zoster ophthalmicus)
Symptoms
- Skin rash
- Skin discomfort
- Headache
- Fever
- Malaise
- Blurred vision
- Eye pain
- Red eye
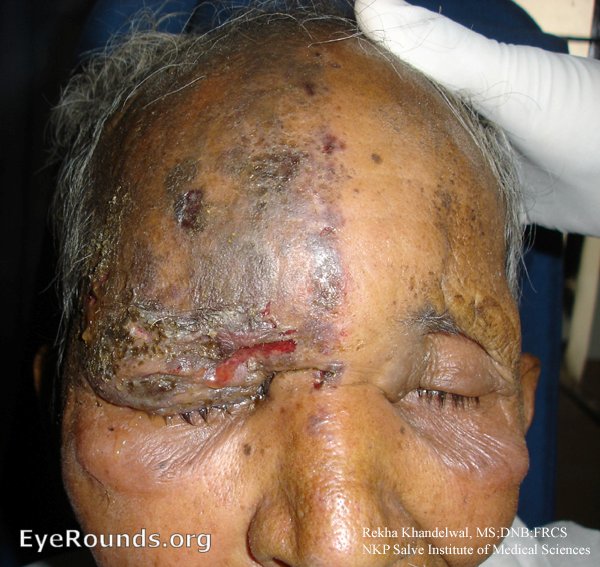
Source: EyeRounds.org. Contributor: Rekha Khandelwal, MS, DNBm FRCS, Department of Ophthalmology, NKP Salve Institute of Medical Sciences and Lata Mangeshkar Hospital, Nagpur.
Signs
- May or may not involve the eye
- More common when side of the nose involved (Hutchinson's sign)
- Conjunctivitis and episcleritis that usually resolve in a week
- May get:
- Keratitis & corneal lesions
- Uveitis & scleritis
- Optic neuritis and extraocular muscle palsies
- Keratitis & corneal lesions
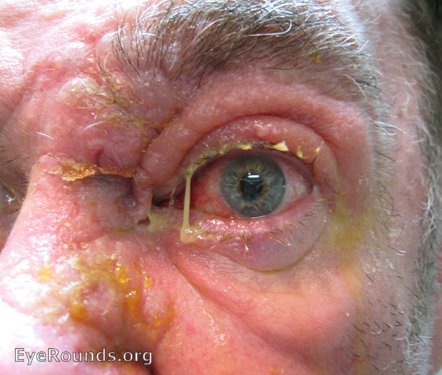
Source: EyeRounds.org. Contributor: Andrew Doan, MD, PhD, University of Iowa.
Skin Lesions
- Initial rash is maculopapular, then vesicular. The vesicles burst and form crusty ulcers.
- Treat with oral aciclovir 800 mg x5 daily for 5 days
Eye treatment
- Oral aciclovir also appropriate for eye, but uveitis and acute corneal lesions may require topical steroids (NOTE: steroid eye drops should only ever be prescribed by an ophthalmologist )
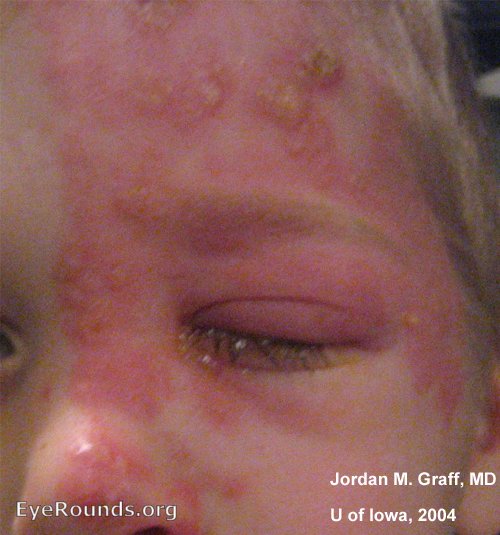
Source: EyeRounds.org. Contributor: Jordan M. Graff, MD, University of Iowa.