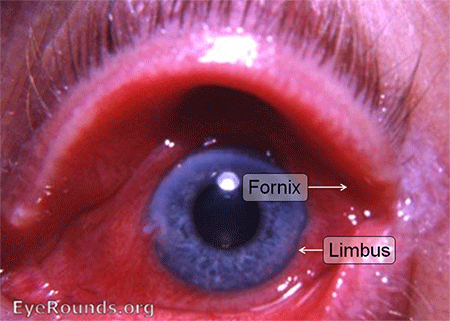
9: Subconjunctival Haemorrhage
History
- Mostly idiopathic
- May be precipitated by trauma, coughing, sneezing, aspirin, hypertension, eye surgery.
Examination
Diffuse or localised area of blood under conjunctiva.
(haemorrhage without a posterior margin may be associated with an intracranial bleed)
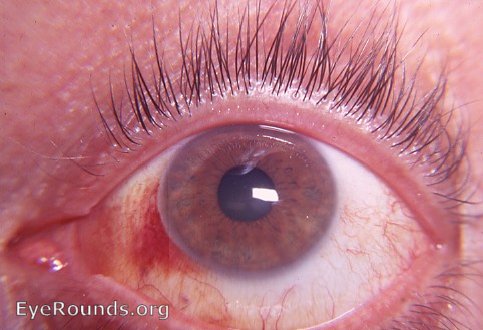
Source: EyeRounds.org. Contributor: William Charles Caccamise, Sr, MD, Retired Clinical Assistant Professor of Ophthalmology, University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry.
Investigation
- Check blood pressure.
- If recurrent, or history suggests bleeding diathesis, request coagulation screen and FBC
Management
- Reassure patient it will resolve without treatment within 10-14 days.