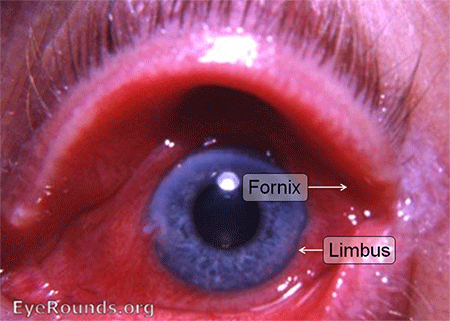
11: Scleritis
Aetiology
50% Idiopathic
50% with systemic associations:
- Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Relapsing polychondritis
- Wegener granulomatosis
- Polyarteritis nodosa
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
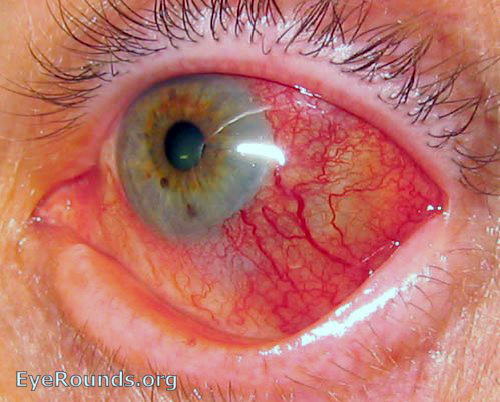
Source: EyeRounds.org. Contributor: Andrew Doan, MD, PhD, University of Iowa.
Symptoms
- Gradual onset
- Severe pain
- Photophobia
- Tearing
- Normal or mildly blurred vision
- Dull, deep, severe pain that can wake patient at night
Signs
- Localised or diffuse scleral hyperaemia, tender to palpation
- Pale areas within red zone can indicate necrotising scleritis
- Possible corneal + intraocular inflammation
Management
Refer to an ophthalmologist for:
- Oral NSAID (Froben) or corticosteroid
- Systemic evaluation by rheumatologist
- Possible cytotoxic agents