4: Injuries from Trauma
Treatment
- Refer immediately to Ophthalmology
- Admit patient
- Protect eye with a shield
- Nil by mouth
- Tetanus if needed
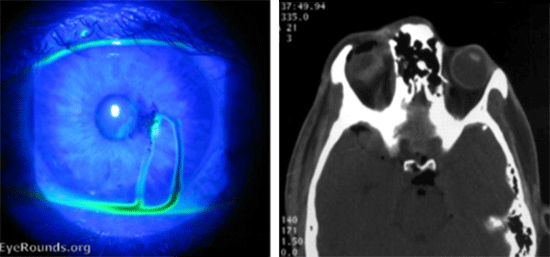
Image credit: Jordan M. Graff, MD. U of Iowa, 2005. EyeRounds.org
- Corneal repair using Nylon sutures or cyanoacrylate glue and a bandage contact lens over the surface
- Usually prescribe oral antibiotics to reduce the risk of endophthalmitis (intraocular infection).
- Intraocular foreign body: Emergency referral to ophthalmology for removal
