Classification of Shunts
- Types of Shunts
- Functional classification
There are four types of shunts:
Click on each title to see a description.
Left to right (ventricular and atrial level)
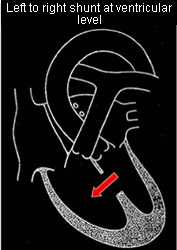
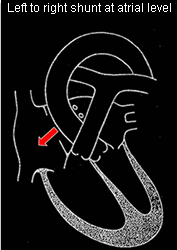
Defects resulting in left to right shunting
Relative incidence:
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD) 28%
- Patent ductus arteriosus 10%
- Atrial septal defect 7%
Bi-directional
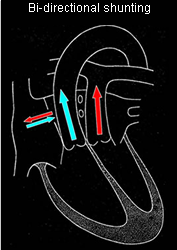
Defects resulting in bi-directional shunting
Relative incidence:
- Transposition 6%
- Tetralogy of Fallot 5%
- Truncus arteriosus 1%
Complete mixing
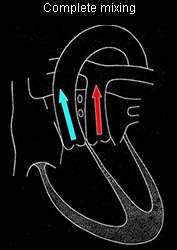
Defects resulting in complete mixing shunting
Relative incidence:
- Pulmonary atresia 2%
- Mitral atresia 1%
- Tricuspid atresia 1%
Right to left (ventricular level)
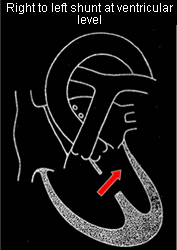
e.g. Tetralogy of Fallot