Radiobiology and the Classification of Biological Effects
Types of cell damage
- Types 1
- Types 2
- Types 3
- Types 4
- Types 5
- Types 6
- Types 7
- Types 8
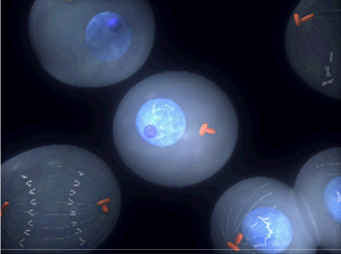
There are different types of cell damage:
- Molecular - Damage to enzymes, RNA and DNA, and interference with metabolic pathways.
- Sub-cellular - Damage to cell membranes, nucleus, chromosomes, mitochondria and lysosomes.
- Cellular - Inhibition of cell division, cell death, transformation to a malignant state.
Tissue /Organ Disruption / life-shortening / cancer.
- Person / Population - Death / life-shortening / genetic damage due to gene and chromosome mutation.
Radiobiology is the study of the effects of radiation on living tissues.
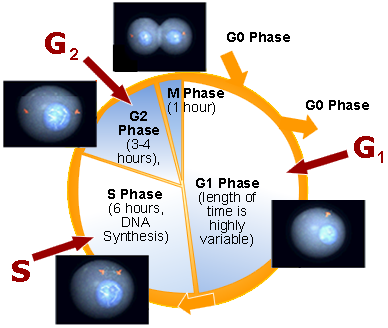
The cell cycle consists of the G, S and M phases.
- Interphase:
- G1 - First Gap
- S - Synthesis
- G2 - Second Gap
- M Phase
Checkpoint genes are active in the G2 phase and if damage is detected, the replication process is delayed until repair occurs.
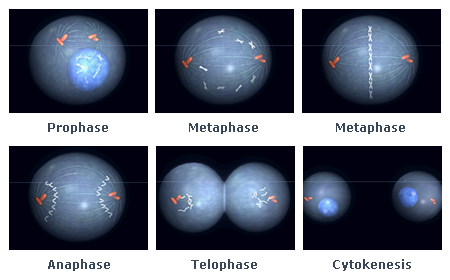
When the cell divides (at mitosis) it is at its most radiosensitive phase. Chromosomal aberrations (changes) due to radiation treatment will inhibit cellular replication and proliferation.
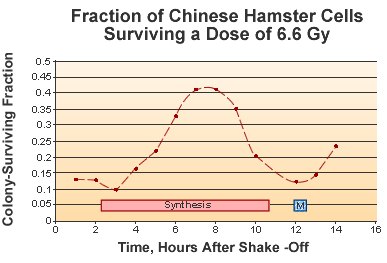
A simple radiobiological experiment can demonstrate the different radiosensitivities of the cell cycle. Chinese Hamster cells can be used to show the response of cells at different stages of the cell cycle can respond to doses of 6.6Gy.
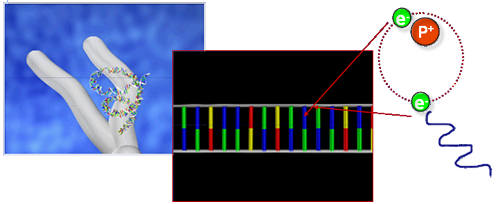
Direct Action of Radiation
When γ rays are absorbed in biological matter, some of t When γ rays are absorbed in biological matter, some of the energy is converted to fast electrons, which can interact directly with the critical targets of the cell - DNA γ rays are already electrons and may also react directly.
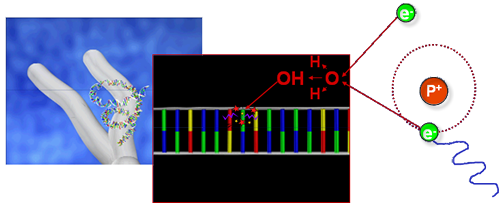
Indirect Action of Radiation
The radiation may interact with other atoms or molecules in the cell to produce free radicals that are able to reach and damage the critical target - DNA may interact with other atoms or molecules in the cell to produce free radicals that are able to reach and damage the critical target - DNA.
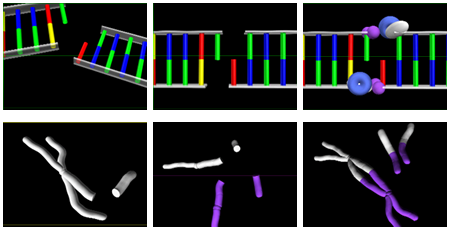
The images on the left show replication due to Chromosonal Abberations:
To watch a video on the different types of cell damage, click the play button (white triangle) below (contains audio).
If you cannot see the video you may require the Flash Player plug-in which can be downloaded from the website (you will need administrator rights on your computer to install it).