Medical Internal Radiation Dose (MIRD)
Steps in the MIRD Calculation
- MIRD Calculation 1
- MIRD Calculation 2
- MIRD Calculation 3
- MIRD Calculation 4
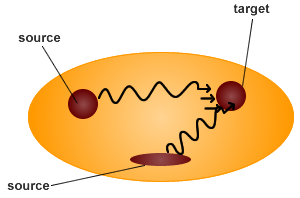
Source and target organs
Below are the steps in calculating the MIRD:
- Consider source organs and target organs –source organs are organs which radioactivity passes or resides through.
- Calculate the cumulative activity in each source organ.
- Look up physical data i.e. mass of target organ, radiation related data.
- Calculate the absorbed dose for each source/target situation:
D = A/m (DSifi), where:
A is the accumulated activity
m is the mass of the target organ
Di is the equilibrium dose constant
fi is the absorbed fraction
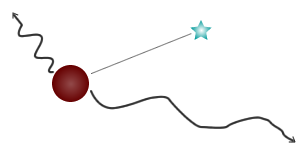
DI (equilibrium dose constant)
Account must be taken of all the different energies and abundances of radiations emitted.
One must not forget that many radionuclides emit tens of different radiations, not just those used in imaging.
DI (equilibrium dose constant) takes account of this.
- Next add up all contributions to a specific target organ to get total dose to that target organ.
- Then do the same for all irradiated organs
- Combine these together using the formulae for effective dose:
E = S {(dose to target organ) x ( tissue weighting factor for this organ)}
summed over all target organs.
A simplification to this process is possible in some cases:
MIRD have a value called ‘S’ - this is the absorbed dose per unit accumulated activity - these are listed in MIRD pamphlet 11.
If there is data that relates to your needs then the calculation becomes:
D = A x S
and hence E as before.