1: Visual Field Defects
Lesions
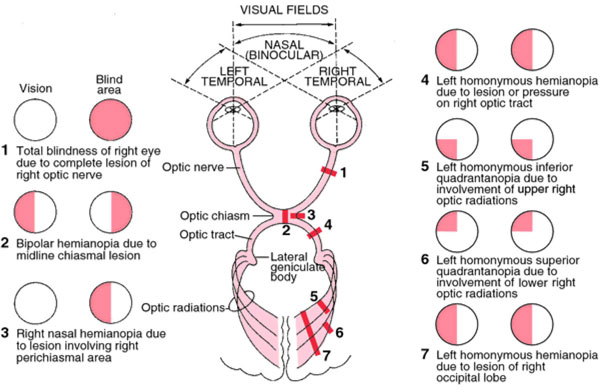
Image credit: Luckmann's Core Principles and Practice of Medical-Surgical Nursing
Rules
- Lesions anterior to the chiasm produce unilateral field defects
- Lesions posterior to the chiasm produce contralateral homonymous defects
- Chiasmal lesions generally produce bitemporal defects.
- The more congruous the defect the more posterior in the visual pathway the lesion
