2: Diplopia (Double Vision)
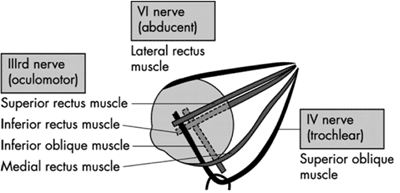
4th (Trochlear) nerve
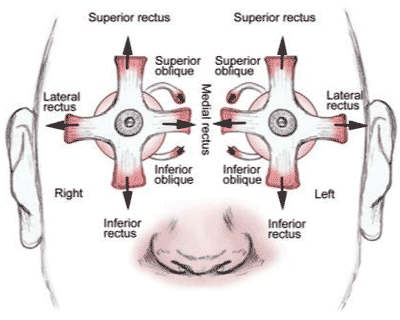
- The 4th (Trochlear) cranial nerve supplies the superior oblique muscle .
- The primary action of the superior oblique is rotation of the eye towards the nose (intorsion)
Differential diagnosis of the causes of a 4th nerve palsy:
A superior oblique palsy can be:
- Unilateral or bilateral
- Congenital or acquired
- Diabetes or hypertension
- Demylinating diseases e.g. Multiple Sclerosis
- Giant cell arteritis
- Tumours
- Aneurysms
Symptoms
Acquired diplopia
Signs
Abnormal head posture (head tilted away from side of lesion) and the eye deviating upwards as it moves towards the nose.
Treatment
- Children Treat any amblyopia and correct refractive error
- Prisms May benefit depending on orthoptic assessment
- Surgery To improve diplopia and occasionally for cosmetic reasons
- Follow up As appropriate