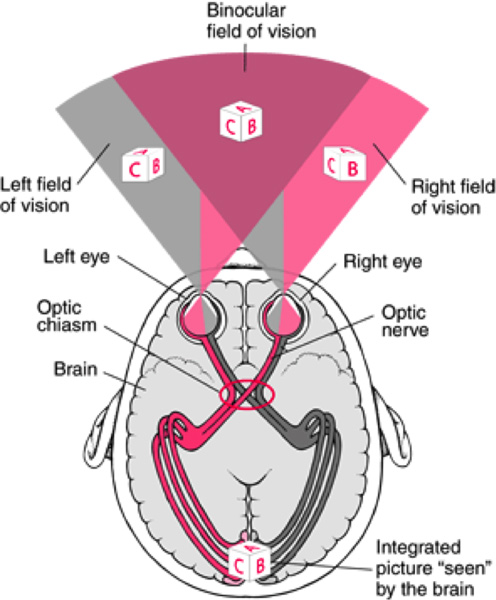
2: Diplopia (Double Vision)
Double vision (diplopia) occurs when the visual axes of the two eyes deviate from fixating straight ahead or become misaligned during eye movement.
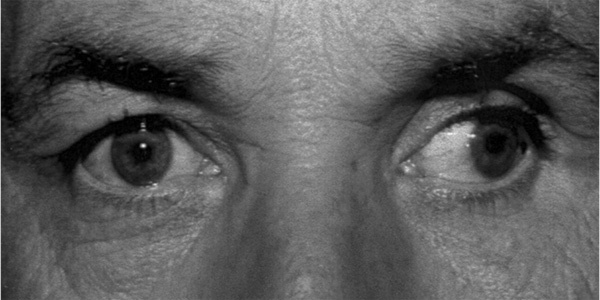
The above patient has misalignment of the visual axies. The left eye deviates outwards when the patient fixates straight ahead showing a left exotropia.
Causes
- Displacement of the globe within the socket
- Tumours
- Trauma
- Infection (Orbital Cellulitis)
- Cranial Nerves Palsies 3rd, 4th ,6th
- From cranial nerve palsies caused by diabetes and hypertension
- Decompensation of latent squint
- Extraocular muscle disease i.e. Myasthenia gravis
- Thyroid Eye disease