Unit 10: Systemic Disease
1: Diabetic Retinopathy
Aetiology
- Hyperglycaemia is the main cause of micro vascular complications, including retinopathy.
- The clinical signs are caused by small blood vessel occlusion, increased vascular permeability and changes in blood vessel walls from loss of supporting pericytes.
- Proliferative diabetic retinopathy occurs in response to vascular endothelial growth factors from ischaemic retina.
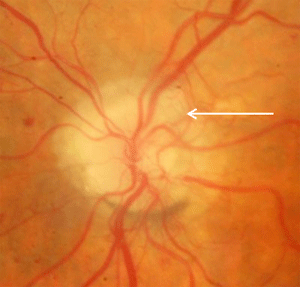
New vessels at the disc (NVD's) occur in proliferative diabetic retinopathy in response to vascular endothelial growth factors, released in response to retinal ischemia.
Source: retinagallery.com
- Signs of diabetic retinopathy are often detected during retinal screening, before symptoms.
- Vision loss is usually caused by maculopathy or vitreous haemorrhage.
- Maculopathy initially can present with slight central visual loss but is often progressive.
- Vitreous haemorrhage often causes acute loss of vision, or floaters in the field of vision.