Unit 10: Systemic Disease
5: Hypertensive retinopathy
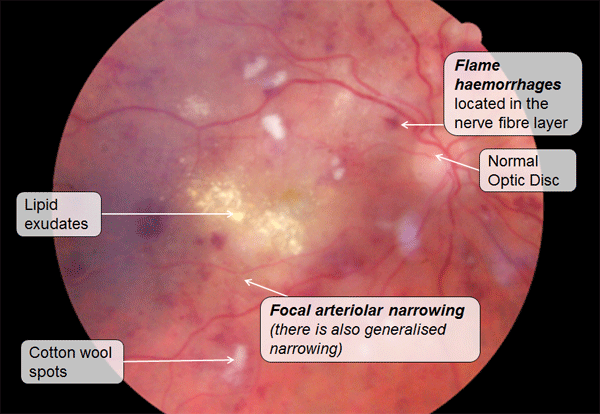
Signs
Signs
of hypertensive retinopathy:
- Focal arteriolar narrowing
- Venous nipping at arteriovenous crossings
- Copper and silver wiring
- Cotton wool spots from small areas of retinal ischemia and swelling
- Lipid (hard) exudates are yellow white intraretinal lipid collections from vascular leakage. At the macula they may resemble a star
- Flame haemorrhages in the retinal nerve fibre layer
- Macular oedema
- Macro aneurysms seen as well defined red dots (sometimes with lipid exudates)
- Optic disc swelling caused by local ischemia